What should be the factor for countries to lift coronavirus lockdown?

Research and Study shows that if lockdown is lifted, COVID-19 will spread rapidly
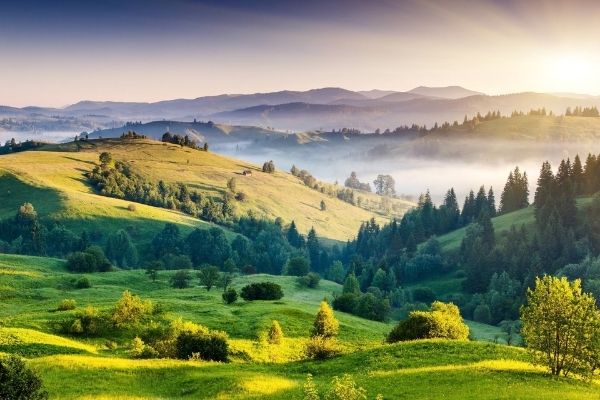
People of many cities, state and countries are currently living in lockdown to break the chain of coronavirus and flatten the curve. China was the first country to impose lockdown in Wuhan province. In the last few days, China has rarely witnessed new cases of coronavirus. China is no longer the country with the highest number of infected people nor with the highest death toll. All eyes are set on China for the upcoming week when the restrictions will gradually fade away.
In Wuhan, which is considered as the epicentre of the outbreak, restrictions are scheduled to be lifted on April 8. But this doesn’t mean that China is done with the virus, the authorities will have a close look to observe if there is any resurgence in cases once the lockdown is lifted.
Research about lifting the lockdown
The trajectory that China follows will be significant takeaways for the rest of the world, especially for the United States of America and European countries who are the new epicentres of the global epidemic.
When the restrictions are lifted in China, it will be seen if the number of COVID-19 cases increases again, and if it increases, will there be a second lockdown in the country.
An article in nature, renowned science journal, says that the virus will have difficulty to resurface as strongly as the first time as most of the people would have already be infected and developed “herd community” as a result.
But this might not be necessary. Taking an example of Wuhan, which accounts for more than half of China’s COVID-19 cases, the majority of people are not infected so when the virus returns, the number of vulnerable people will be still high.
Read more: Various countries are releasing prisoners amid coronavirus, Here’s why?
So, it is important for state and central governments to lift the restrictions gradually along with regular monitoring, testing and contact tracing.
A study by COVID-19 response team published in London’s Imperial College says that 11 European countries – UK, Spain, Norway, Denmark, Italy, Norway, Belgium, Austria, Germany and Switzerland, where social distancing was practised, the reproduction number (number of people an average COVID-19 infected person infects) has come down.
The study suggests that the number of infected people in many countries are under-reported because testing is limited to hospital settings and not being done at the community level. They estimated that 6,00,000 people may be infected in Germany but the official report in Germany is only 84,000.
This means that the populations in many countries are not close to attaining herd immunity, implying that lifting restrictions will enable the virus to “spread rapidly”.
Have a news story, an interesting write-up or simply a suggestion? Write to us at info@oneworldnews.com